Facade engineers and architects are at the forefront of a sustainable revolution in building design, leveraging 3D printing technology with eco-friendly materials like Ultrafuse® rPETG Pellets. This innovation allows for the creation of customized, energy-efficient facade elements that integrate multiple functions into single components. The technology enables the production of translucent, recyclable facades with complex geometries, optimizing resource consumption and enhancing aesthetic possibilities. Professionals in this field are now able to design for disassembly and material recovery, aligning with circular economy principles while pushing the boundaries of architectural expression and performance.
Recycled, Reimagined, and Rebuilt
Closing the Loop with 3D Printing
Ultrafuse® rPETG Pellets: A Game-Changer for Sustainable Architecture
Ultrafuse® rPETG Pellets are revolutionizing sustainable 3D printing in architecture. Made from traceable, food-safe recycled materials, these pellets offer excellent surface quality, transparency, and mechanical properties. They’re ideal for large-scale additive manufacturing, providing cost-effective and time-saving production of facade components. The material’s translucent quality allows for creative lighting effects, as demonstrated in recent architectural projects (1).
Recycled Polymers and Aluminum from Beverage Cartons
Innovative approaches are emerging to utilize waste materials in facade construction. For instance, recycled polymers and aluminum from beverage cartons are being repurposed for 3D printed facades. This approach not only reduces waste but also creates unique aesthetic possibilities for building exteriors.
Bio-Based and Biodegradable Materials in Facade Printing
Researchers are developing bio-based materials for 3D printed facades that can be processed without artificial adhesives. For example, a bio-based adhesive called “Biomix” utilizes waste and secondary products from the wood industry. This material enables the production of fully recyclable wall components through additive manufacturing, establishing a closed material cycle in timber construction. Additionally, bioplastics made from renewable sources like corn starch or sugar cane are being explored for facade cladding, offering weather resistance and durability while reducing the need for limited natural resources.
3D printed concrete
3D printed concrete facades have made significant strides in recent years, with several notable examples showcasing the technology’s potential for sustainable and innovative architecture:
BESIX Headquarters in Dubai: Completed in 2020, this project features one of the world’s largest 3D printed concrete façade. The facade consists of 290 panels, each taking about 10 minutes to print (2). This project demonstrates the scalability and efficiency of 3D printing technology for large-scale architectural applications.
One South First Building in Brooklyn: While not entirely 3D printed, this 45-story building utilizes 3D printed tooling to create its unique concrete facade. The design, reminiscent of sugar crystals, pays homage to the site’s history as a sugar refinery. The 3D printed molds used for casting the concrete elements could be reused up to 200 times, significantly more than traditional wood molds (3).
(1) https://forward-am.com/use-cases-and-whitepapers/sustainable-3d-printed-architecture-with-recycled-ultrafuse-petg-pellets/
video: https://youtu.be/RWrp9HQpQdc?si=yPbv3Jlpv0hs8RWi
(2) https://www.besix.com/en/news/besix-3d-prints-largest-concrete-facade-in-the-world
(3) https://www.additivemanufacturing.media/articles/concrete-facade-made-with-3d-printed-tooling-now-complete
video: https://vimeo.com/344411135/c7193b7a58?share=copy
Sustainable Facades of the Future
The Role of 3D Printing
Enhancing Energy Efficiency and Sustainability in 3D Printed Facades
Passive Design Elements for Optimized Resource Consumption
3D printing technology enables the creation of complex geometries that optimize resource and energy consumption in building facades. The E3D project, set to run from June 2024 to May 2027, focuses on developing passive facade elements that address climate variability and moisture-related damage challenges (1). These elements can be customized to redirect air flow and incorporate thermal mass, enhancing the facade’s overall energy efficiency.
Integration of Active Facade Solutions
The E3D project also aims to incorporate active facade solutions alongside passive elements. This integration changes the role of the building envelope in energy efficiency, potentially including features like embedded sensors or adaptive shading systems. Such solutions can dynamically respond to environmental conditions, further optimizing energy use.
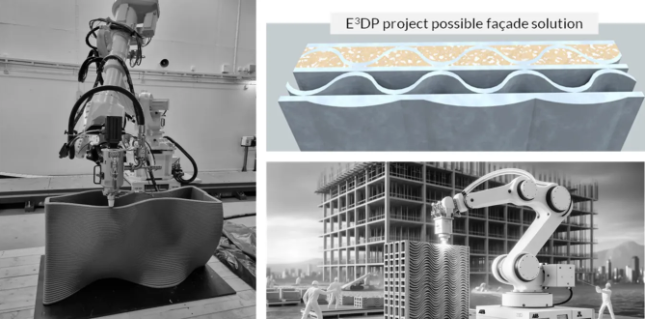
Circular Economy Principles in Facade Design
Designing for Disassembly and Material Recovery
3D printed facades offer opportunities for designing components that can be easily disassembled and recycled at the end of their life cycle. This approach aligns with circular economy principles, reducing waste and enabling the recovery of materials for future use (2).
Closed-Loop Material Systems in Facade Production
Research is ongoing into the use of recycled materials in 3D printed facades. For instance, studies have shown that replacing up to 50% of natural coarse aggregate with recycled construction and demolition waste can produce concrete with good mechanical, durability, and hygrothermal properties (3). This closed-loop approach significantly reduces the environmental impact of facade production while maintaining high performance standards.
(2) https://www.mdpi.com/2075-5309/15/2/189
(3) https://jfde.eu/index.php/jfde/article/view/193
Breaking Barriers
Innovative Composite Applications for a Greener Tomorrow
3D printing technology offers unprecedented precision and customization in facade element production. As Moritz Mungenast, architect and CEO of Mungenast/Morroni notes, “With 3D printing, we can create customized designs that are like a tailored suit for each building,” allowing for the integration of insulation, ventilation, and acoustic optimization into a single component. This approach not only reduces production steps but also enables the seamless link between digital design and production, with components ready to use straight from the printer.
Structural Performance and Durability
To ensure the safety and reliability of 3D printed facade components, rigorous testing and certification processes are essential. UL 3401 is used to evaluate and confirm that a fabricator’s 3D printing equipment, material, and fabrication process consistently produce building elements that maintain the same integrity as the initially tested samples. This certification helps demonstrate compliance with fire, building envelope, indoor air quality, and other building code requirements.
The long-term performance of 3D printed facades in various climate conditions is a critical consideration. Ongoing research, such as the SPONG3D project, aims to develop 3D-printed facade panels that integrate insulating properties with heat storage in complex, mono-material geometries. These developments focus on optimizing thermal performance and adaptability to different climatic challenges.
Aesthetic Possibilities of 3D Printed Sustainable Facades
The freedom of form offered by 3D printing unlocks new possibilities for customized branding and artistic expression in facade design. 3D printing even enables the creation of translucent facade elements using recycled materials, transforming waste into high-quality architectural solutions. Architects and designers can now create elaborate patterns, intricate textures, and captivating geometries that were previously impossible with traditional construction methods. Each project becomes a unique work of art, showcasing the marriage of technology and creative expression in urban landscapes.
Useful links:
https://www.cemexventures.com/3d-printing-in-construction/
As the Editor of FacadeToday.com, I merge my passion for Design, Architecture and Technologies with three decade of experience collaborating with entrepreneurs across many industries. My career has centered on fostering innovation, scaling business opportunities, and bridging gaps between technical experts, business developers, and creative visionaries. I thrive at the intersection of sustainable solutions, material advancements, and smart technologies, curating insights on themes like energy-efficient facades, smart tech, and advanced manufacturing. With a commitment to lifelong learning, I aim to empower architects and facade engineers by translating innovations into actionable knowledge, driving the industry forward through purposeful connectivity and cutting-edge practices.





